A. Read the following passage:
Robi is reading a story book. The book is written by a famous writer of Bangladesh. Robi likes stories about the freedom fighters in the book. Our freedom fighters are honoured by the whole world. They sacrificed their life for our motherland.
There are two types of sentences in the above passage.
Notice the sentence:
Robi is reading a story book.
Subject verb object
It is in the active voice. The subject here is the doer of an action.
Notice the sentence:
The book is written by a famous writer of Bangladesh.
Subject — verb ------------ doer of the action
It is in the passive voice. The subject (the book) here is the 'receiver' of the action. It does not perform any action.
More examples:
Active: The ball hit Jessica.
Passive: Jessica was hit by the ball.

Active: Jahid wrote a letter.
Passive: The letter was written by Jahid.

Active: John took a picture.
Passive: A picture was taken by John.

Note: To change an active sentence into a passive one:
a) If we want to specify who is the 'doer' in a passive sentence, we use 'by' after the main verb in an assertive sentence and then mention the agent.
For example:
Active: Mira broke the glass.
Passive: The glass was broken by Mira. (by +agent)
Structure:
Active sentence: subject + verb+ object
Passive sentence: subject+be + past participle + by + agent
b) Sometimes agents are not mentioned in the passive voice. For example:
Active : People speak English all over the world.
Passive: English is spoken all over the world.
B. Look at the following changes. If there are pronouns as subject in the active voice, they change their forms in the passive voice.
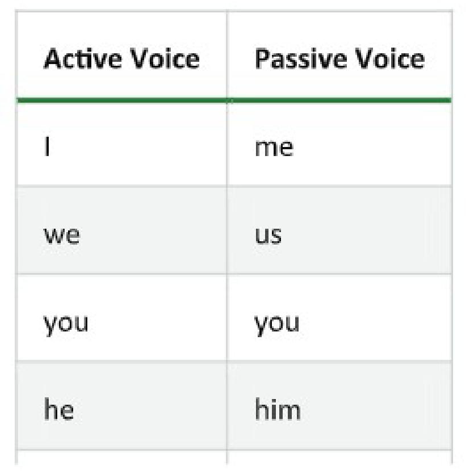
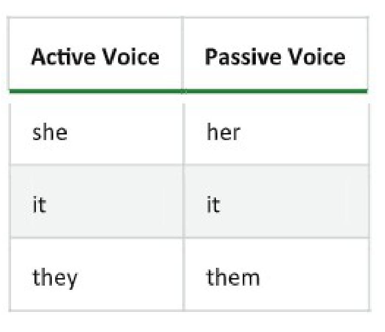
Some sentences have a direct and an indirect object. Rewriting an active sentence with two objects in the passive voice means that one of the two objects becomes the subject, while the other one remains an object. Which object you will change into the subject depends on what you want to put the emphasis on.
We can change it in two ways:
Active : The teacher taught us English.
Passive : i) English is taught to us by the teacher.
ii) We are taught English by the teacher.
Active : Mother told me a story.
Passive : i) A story was told me by mother.
ii) I was told a story by mother.
More examples:

Note:
The object of the active verb becomes the subject of the passive verb. Therefore, sentences which do not have an object cannot be changed into the passive. The following sentences, for instance, CANNOT be changed into the passive because they do not have objects.
The old man sat on the floor.
The child sleeps.
The wind blows.
The dog barks.
Fire burns.
He laughed aloud.
C. Read the following passage and underline the active and passive verbs:
The Sonargaon folk museum was built in the area named Narayangonj. It has been artistically decorated for the visitors. It stores many archaeological things including Bronze statues and caskets, terracotta plaques, utensils, coins, jewelries, pottery etc. They have a great historical value. The government has taken many steps to enhance the facilities for the visitors.
D. Use the following verbs in active and passive forms:
touch, invite, decorate, touch, break, request
E. Change the sentences into the passive voice. Mention the tense of the verb.
Our new teacher teaches us English. Now he is teaching us a new lesson. We have completed the lesson on paragraphs. We are practicing the new lesson. Our teacher taught us the skills of learning language. Last week we were practicing pronunciation. We had learnt the uses of articles before we learnt the rules. We will write a paragraph tomorrow.
A. An interrogative sentence in the active voice will remain interrogative in the passive voice. We form passive questions by putting the auxiliary verb before the subject (according to the tense). Then we place the subject and the past participle form of the main verb.
The following example shows how the voice of interrogative sentences is changed:
Does your brother draw a picture?
Is a picture drawn by your brother?
If the question in the Active Voice begins with an auxiliary verb, the Passive voice must also begin with a suitable auxiliary verb. If the question begins with a 'wh' question word (what, when, how...), the Passive Voice must begin with the same.
Look at the following changes:
Active Voice Passive Voice
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
| Are you reading a book? | Is a book being read by you? |
| Has she cooked the food? | Has the food been cooked by her? |
| Will you close the door? | Will the door be closed by you? |
| Who broke the glass? | By whom was the glass broken? |
| Why did you write such a letter? | Why was such a letter written by you? |
| Where can you keep the box? | Where can the box be kept by you? |
Where can you keep the box? Where can the box be kept by you?
Passive Structure: (question word) auxiliary verb+ object of the active verb + past participle form of the main verb + by + subject of the active verb
Change the following sentences into the passive form :
Now we will change assertive sentences, negative sentences and interrogative sentences into their passive forms in different tenses :
Present Simple TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: am/is/are | |
Active voice: Utsho sings Nazrul songs. Utsho does not sing a modern song. Does Utsho sing any kind of song? | Passive voice: Nazrul songs are sung by Utsho. A modern song is not sung by Utsho. Is any kind of song sung by Utsho? |
Present Continuous TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: am being/is being/are being | |
Active voice: I am writing a letter I am not writing a letter. Am I writing a letter? | Passive voice: A letter is being written by me. A letter is not being written by me. Is a letter being written by me? |
Present Perfect TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: has been/have been | |
Active voice: She has finished her work. She has not finished her work. Has she finished her work? | Passive voice: Her work has been finished by her. Her work has not been finished by her. Has her work been finished by her? |
Past Simple TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: was/were | |
Active voice: I killed a snake. I did not kill a snake. Did I kill a snake? | Passive voice: A snake was killed by me. A snake was not killed by me. Was a snake killed by me? |
Past Continuous TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: was being/were being | |
Active voice: He was drawing a picture. He was not drawing a picture. Was he drawing a picture? | Passive voice: A picture was being drawn by him. A picture was not being drawn by him. Was a picture being drawn by him? |
Past Perfect TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: had been | |
Active voice: They had completed the assignment. They had not completed the assignment. Had they completed the assignment? | Passive voice: The assignment had been completed by them. The assignment had not been completed by them. Had the assignment been completed by them? |
Future Simple TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: will be | |
Active voice: She will buy a watch. She will not buy a watch. Will she buy a watch? | Passive voice: A watch will be bought by her. |
Future Perfect TenseAuxiliary verbs in passive voice: will have been | |
Active voice: You will have started the job. You will have not started the job. Will you have started the job? | Passive voice: The job will have been started by you. |
Note: Passive voice is not usually used in the following tenses :
B. Fill in the blanks according to the mentioned tenses. Use the appropriate forms of verbs given in brackets:
C. Read the following sentences and say whether they are in the active or in the passive voice. Write down the tense of each sentence:
a. The thief was caught.
b. The boy drew a picture.
c. The bird was killed by a cruel man.
d. I read my English grammar book.
e. The field is ploughed.
d. The book is lost.
e. People will soon forget it.
f. The window is broken.
g. I was ordered to bring the book.
h. Who taught you math?
A. An imperative sentence expresses an order, a request, a piece of advice or a suggestion.
The imperative sentence in the passive voice has the following structure:
Let + object + be + past participle
When the active voice begins with do not, the passive voice has the following structure:
Let not + object + be + past participle
In some sentences it is possible to put not after the object or be.
Examples are given below:
Active: Bring it home.
Passive: Let it be brought home.
Active: Do it at once.
Passive: Let it be done at once.
Active: Do not beat the dog.
Passive: Let the dog not be beaten.
Active: Let me do it.
Passive: Let it be done by me.
B. Now write a passive sentence for each of the following active sentences:

A. The passive voice is usually used:
To describe a process, an event, an incident, an advertisement, an announcement and a notice
Examples:
a) process of making a sandwich: The butter should be soft. Crusts may be removed or left on according to taste.
b) event: Our annual sports will be held on 2 November.
c) incident: The annual cultural program of the school will be held on 20 May.
d) advertisement: Your comfort is ensured in your journey with us.
e) announcement: Prizes will be given by the honourable minister.
f) notice: The exam will be held on 2 5 June.
B. Look at the picture and fill in the gaps in the following sentences in passive form with the given verbs in the bracket.

a. The walls are not ______ (paint).
b. A table is _____ in the middle (place).
C. The chairs ______ properly (arrange).
d. A lampshade _____ from the roof (hang).
e. A large refrigerator _____ with the wall (attach).
C. Make the following sentences active:
D. Choose the right option:
common.read_more